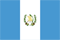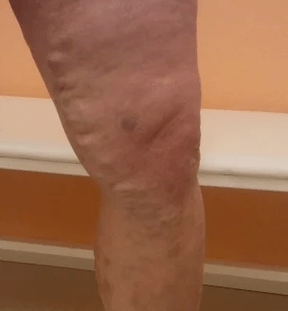
Varicose veins- This is the expansion of a subcutaneous vein with a diameter of more than 3 mm.Varicocele veins form varicose veins due to impaired operation of the venous valve.At the same time, blood flows out of the lower limbs and the pressure inside the veins increases, which may lead to chronic venous insufficiency.
Sometimes, telanggitictia and reticulum veins are mistaken for varicose veins.
These are veins of diameter3mm and below, They do not affect venous outflow, but will lead to clear cosmetic defects.
What is the prevalence of varicose veins?
30% of women and 15% of mature age men have dilated varicose veins.The prevalence of varicose veins in the lower limbs increases significantly with age and is in most people over the age of 60.The proportion of nutritional diseases in adulthood is only 1.8%, while in the elderly, the indicator reaches 20%.Meanwhile, every fifth patient in life faces thrombophlebitis.One of the causes of disability is that the share of veins in people with disabilities is not just arteries.
The main risk factors for developing varicose veins are:
- Old age
- female
- Pregnant
- Hormonal diseases
- Positive family history
Other risk factors:
- Smoking
- Arterial hypertension
- constipate
The literature on other risk factors is contradictory.In addition, the risk of developing venous disease is very low.
How do varicose veins manifest?

The most common manifestation is the uneven veins protruding above the surface.In some cases, they are almost non-obvious or determined only by touch, while in other cases, they are similar to large grape bunches in the formation or appearance of nodes.
Usually, varicose veins are accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Feeling and tension of legs
- Pain pulling and/or soreness along the veins
- Rapid fatigue of legs
- Itching of leg skin
Very few varicose veins can cause uneasy leg syndrome and nighttime leg cramps.
What are the dangers of varicose veins progress?
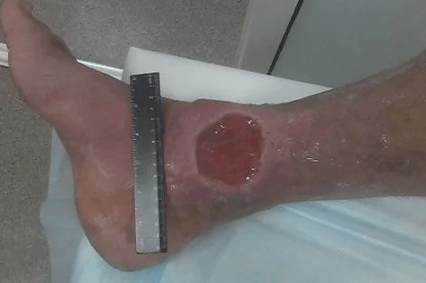
In the absence of treatment, progression of varicose veins can lead to chronic venous insufficiency (CVN).The presence of HVN indicates a serious violation of lymphatic venous return (clinical C3-C6 CAP classification), which includes: chronic edema (lymph), skin pigmentation changes (pigmentation), venous eczema, skin compaction, nutritional varicose ulcers.
What are the complications of varicose veins?
Thrombosis - The formation of thrombosis in the surface venous system is an event that faces 20% of patients with varicose veins.This thrombosis is accompanied by severe pain, redness in the skin, sealing along the veins of the lower legs and/or thighs.In the absence of treatment, a thrombotic mass that can enter the deep vein system.
Deep vein thrombosis (TGV)- In most cases, the beginning of the process is asymptomatic.When a thrombus develops a vein in the femoral segment and pelvis, the main outflow of blood from the lower limbs is disturbed, accompanied by severe edema and pain syndromes, which are considered a life-threatening condition.
trombolism (TELA) of pulmonary artery- In 10% of cases, a thrombotic mass in the deep veins of the lower limbs is shattered and migrated with blood flow to the pulmonary artery, resulting in death.
What is required for a correct diagnosis?
Given the various forms of venous disease, the development of the disease and every detail of the history of the patient's life, the consequences of the disease, transaction, external examinations of the doctor and the most important thing is ultrasound, ultrasound, ultrasound, ultrasound, ultrasound veins, ultrasound scans of the veins, are important for making the correct diagnosis.Today, the latter is the most useful accurate and non-invasive method for studying lower limb veins.
Varicose veins treatment, the most common method:
- Drug treatment of vegetarian drugs have demonstrated their effectiveness in reducing symptoms of varicose veins, but they cannot eliminate varicose veins by themselves.Drug therapy is successfully used to prevent risk group complications, preoperative preparation and postoperative rehabilitation.
- Compression processing- Special medical knitted clothing in golf, socks, tights.In some cases, multi-layer bandages with elastic bandages with various extensions and hardware pneumonia compression are used.The role of compression treatment is difficult to overestimate, and it exists in almost every stage of preventing and treating chronic veins.
- Introduce the cavity of the drug vein that may cause it to close.This method is the gold standard for eliminating reticulum veins.It is successfully used to treat varicose veins of non-diameter and is limited in eliminating pathological blood flow from major subcutaneous veins.
- Classic operation- Modern performance combined with venectomy is performed on an outpatient basis under spinal or local anesthesia.In some cases, this is the only viable way to have a target vein that is very persuasive and/or has high expansion.However, this method is not as good as the abdominal trauma procedure.
- Neto Vein Laser Prison- A method of treating varicose veins in which the veins are not removed but are closed from the inside with the energy radiated from the laser, which is directly brought into a wholesale container with fibers.The effectiveness of this process is comparable to the results of surgical vein removal, while it is characterized by minimal trauma.The recovery time is 1-3 days.
- Radio frequency prison- A progressive method to eliminate pathological blood flow in the subcutaneous vein of the trunk.This is a complete outpatient procedure under local anesthesia.The effectiveness of the treatment corresponds to the level of classical veinectomy, with the pain syndrome being minimal or absent.The recovery time is 1-2 days.